Project update 4 of 14
Battery Life Estimation Example
by Prajay MadhavanIn this example, we’ll determine the current draw characteristics of a wireless mouse and use those measurements to estimate the expected lifetime of two types of batteries.
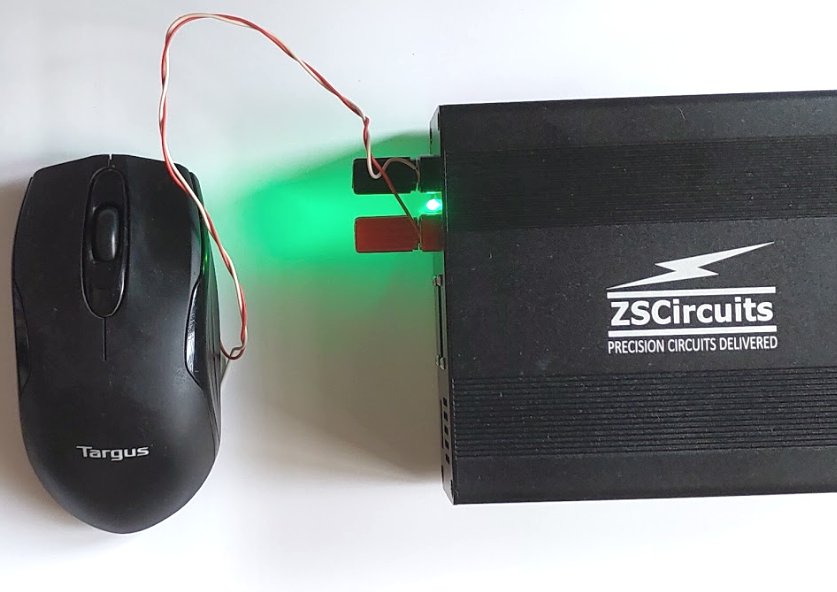
A wireless mouse made by Targus is used in this experiment. The AA battery is removed from the mouse and it is powered directly by the ZS1100A, with the output set to 1.5 V. The mouse is used normally during the measurement which extends to about 75 seconds.
Current Profiling
Measurement setup
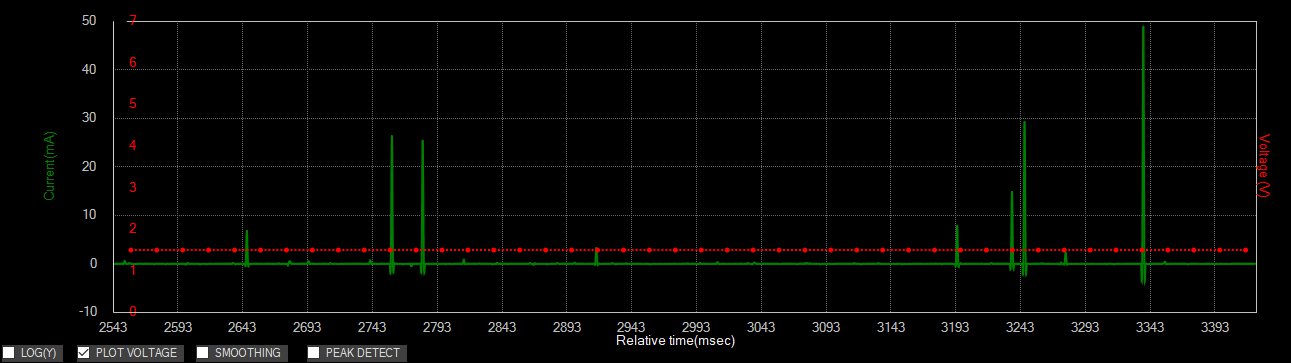
Measurement data
The current draw consists of very short pulses lasting just few microseconds. This type of current profile is very difficult to measure using other equipment due to limitations in bandwidth. Note that the current rises from a few μA to several ten of mA in few microseconds. The ZS1100A captures these current signals with ease.
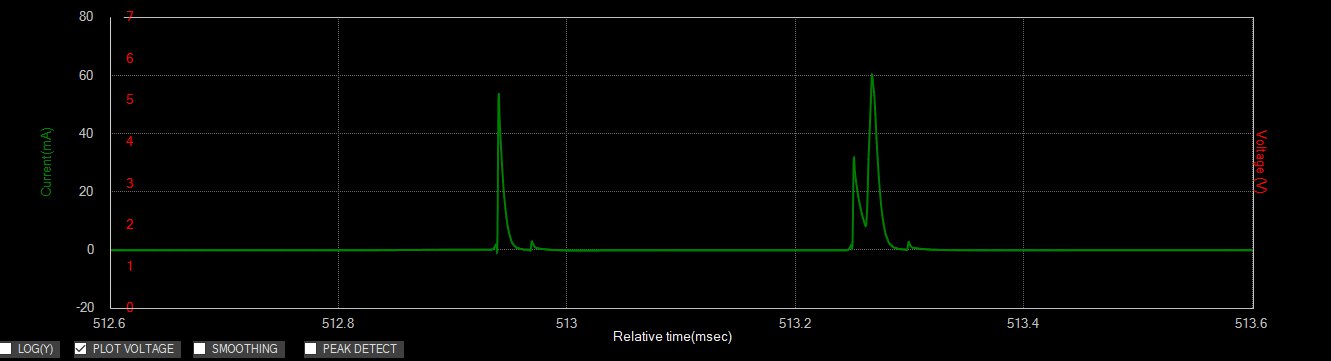
Zooming in on the measurement shows the narrow pulses. These pulses are observed whenever the mouse is moved or a button is clicked. The mouse transmits this information to the PC using the sub-GHz wireless link in short bursts. These bursts can be clearly captured and measured by the ZS1100A.
Battery Life Estimation
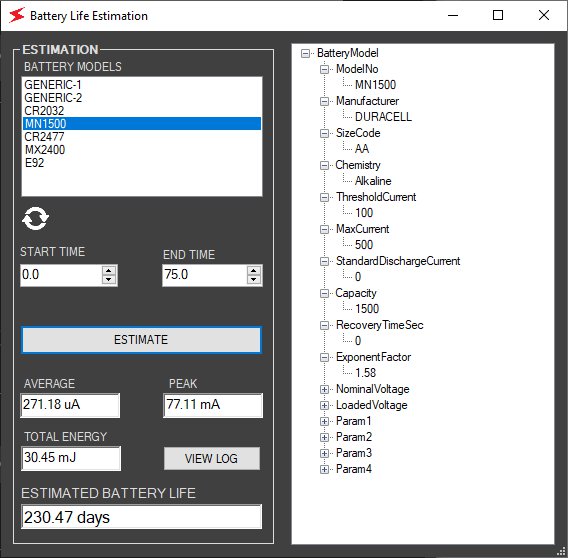
Battery life estimation with an MN1500, AA, 1.5 V battery
Using the current profile and an appropriate battery model in the ZS1100A software, the overall battery life of this wireless mouse can be determined very easily. In this experiment, we infer that a single MN1500 AA battery will last for about 230 days with this typical usage.
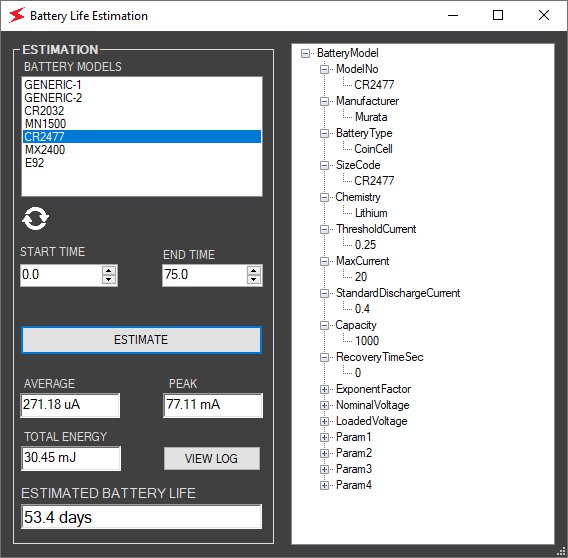
Battery life estimation with CR2477, 3 V battery
The same current profile can then be used with other battery models - in this case, a CR2477. For the sake of simplicity, we assume that the same current is drawn from the 3 V battery as from the 1.5 V. Ideally the current should have halved with the scaling in voltage, but that does not matter in this context as we are demonstrating the battery model.
The CR2477 has a capacity of 1000 mAh, so a simple calculation using the battery capacity and average current would yield a life span of about 154 days.
Life = 1000 mAh / 0.27118 mA / 24 h = 154 days
But when the current profile is applied to the battery model, we get an estimation of 53.4 days. A difference of 100 days over the simple model.
Measurements with the CR2477 model shows a much shorter life due to its limited peak-current capability and capacity degradation at high currents. This effect is clearly captured with our realistic battery models and battery life estimation algorithm.
Thus, the ZS1100A provides a more realistic and practical estimation of battery life, which is quite close to the real-world observations.